Taking CVD Diagnostics to the Next Level
Boston Heart Diagnostic’s foundational CVMap provides more comprehensive insight into CVD risk by augmenting standard lipid assessment with advanced diagnostics.
The unique combination of biomarkers – lipids and Lp(a) levels, as well as lipid particle numbers; markers of inflammation; and BHD’s unique Cholesterol Balance reporting are informative and readily actionable.
CVMap is designed to be easily incorporated into your practice to guide treatment and to motivate your patient’s lifestyle journey. Boston Heart also offers clinician access to experienced Medical Science Liaisons, as well as a personalized Diagnostic Booklet, Life Plan, RD access and app support for your patients.
 Advanced Lipid Markers
Advanced Lipid Markers
Routine lipid testing alone is inadequate to identify and monitor the threat of CVD. Studies suggest select advanced lipid biomarkers enhance the understanding of a patient’s risk.
- sdLDL-C
- ApoB
- Lp(a)
 Markers of Inflammation
Markers of Inflammation
- hsCRP
- LpPLA2
 Additional Insights
Additional Insights
- Cholesterol Balance
unique to BHD that provides insight into intervention + monitoring
An Introduction to CVMap in Practice
Join Dr. Regina Druz, MD as she explores the new CVMap Panel with clinical cases highlighting ways to best utilize this foundational cardiovascular panel.
Boston Heart Diagnostic’s foundational CVMap provides more comprehensive insights into CVD risk by augmenting standard lipid assessment with advanced diagnostics. Combine advanced lipid markers, markers of inflammation and additional insights with cholesterol balance.
Watch the video:
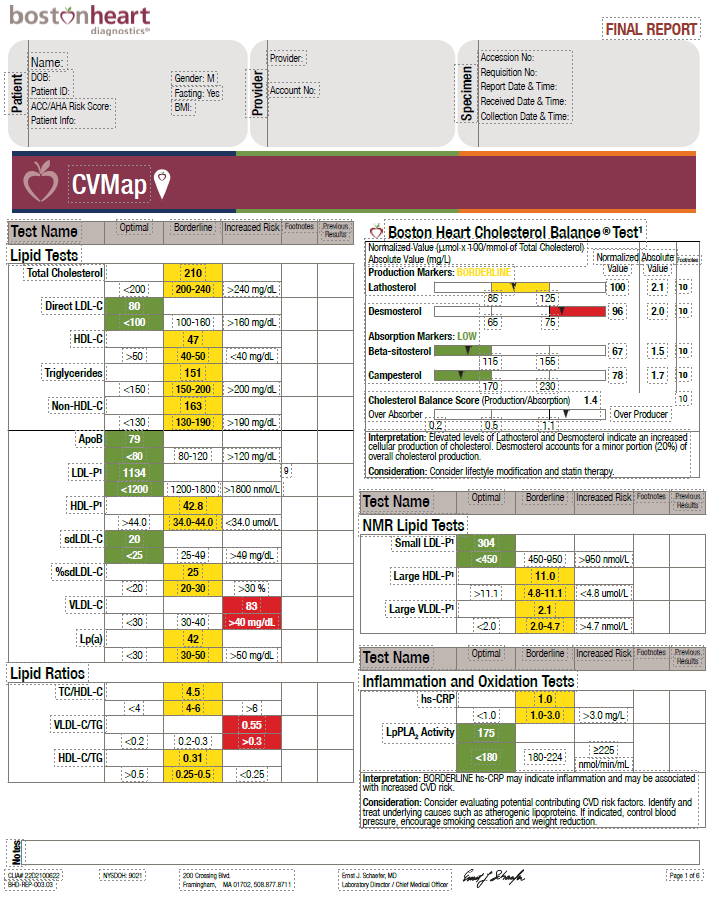
 CVMap Components
CVMap Components
Order Code 87300
| BioMarker | BioMarker Description |
|---|---|
| Lipids | |
| Total cholesterol | Amount of cholesterol in all cholesterol-containing lipoproteins. |
| Direct LDL-C | Direct measurement of the amount of cholesterol in atherogenic low-density lipoproteins. |
| sdLDL-C | Amount of cholesterol in the densest and most atherogenic LDL particles. Stronger predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) than apoB or LDL-P. |
| HDL-C | Amount of cholesterol in high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Higher levels of HDL are associated with reduced CVD; however, very high concentrations have shown increased risk for adverse outcomes in certain populations. |
| Triglycerides | Elevated levels increase CVD risk by altering lipoprotein metabolism. |
| NonHDL | Calculation that represents the cholesterol carried by all atherogenic particles. It is an independent risk factor for ASCVD, especially in patients on statin therapy and/or with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. |
| TC/HDL-C | Lipid ratio that is a stronger risk factor than LDL-C or HDL-C. |
| HDL-C/TG | Lipid ratio associated with insulin resistance. |
| apoB | Major protein component of LDL-C and other atherogenic lipoproteins. |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein particle similar to LDL-C that contains an additional protein called apolipoprotein(a). Independent, predominantly genetically determined, and prevalent causal risk factor for atherosclerotic heart disease. |
| LDL-P | Total number of LDL particles in blood. High levels of LDL-P are a strong, independent predictor of CVD. |
| HDL-P | Total number of HDL particles in blood. Lower concentration of HDL particles has been independently associated with coronary artery disease (CAD) risk. |
| Small LDL-P | Total number of small low-density lipoprotein articles in blood. A higher level of small LDL-P has been seen to be elevated in individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. |
| Large HDL-P | Amount of large high-density lipoprotein particles in blood. Studies suggest a strong association between HDL-P size and risk factors characteristic of the metabolic syndrome. |
| Large VLDL-P | Amount of large low-density lipoprotein particles in blood. |
| Cholesterol Balance | |
| Production Markers | Elevated lathosterol and desmosterol indicate cholesterol over-production and can be treated with agents that reduce production. |
| Absorption Markers | Elevated beta-sitosterol or campesterol indicate cholesterol over-absorption and can be treated with agents that reduce absorption. |
| Inflammation | |
| hs-CRP | Acute phase inflammatory protein associated with atherosclerosis (after other causes excluded). |
| LpPLA2 | Enzyme produced by monocytes/macrophages that reflects an active inflammatory process in the vessel wall. |

Boston Heart Diagnostics is transforming the treatment of cardiovascular disease and related diseases with novel diagnostics, reports, and a personalized, scientifically designed nutrition and lifestyle program that have the power to change the way healthcare providers and patient communicate about heart health.
© Boston Heart Diagnostics. All rights reserved.